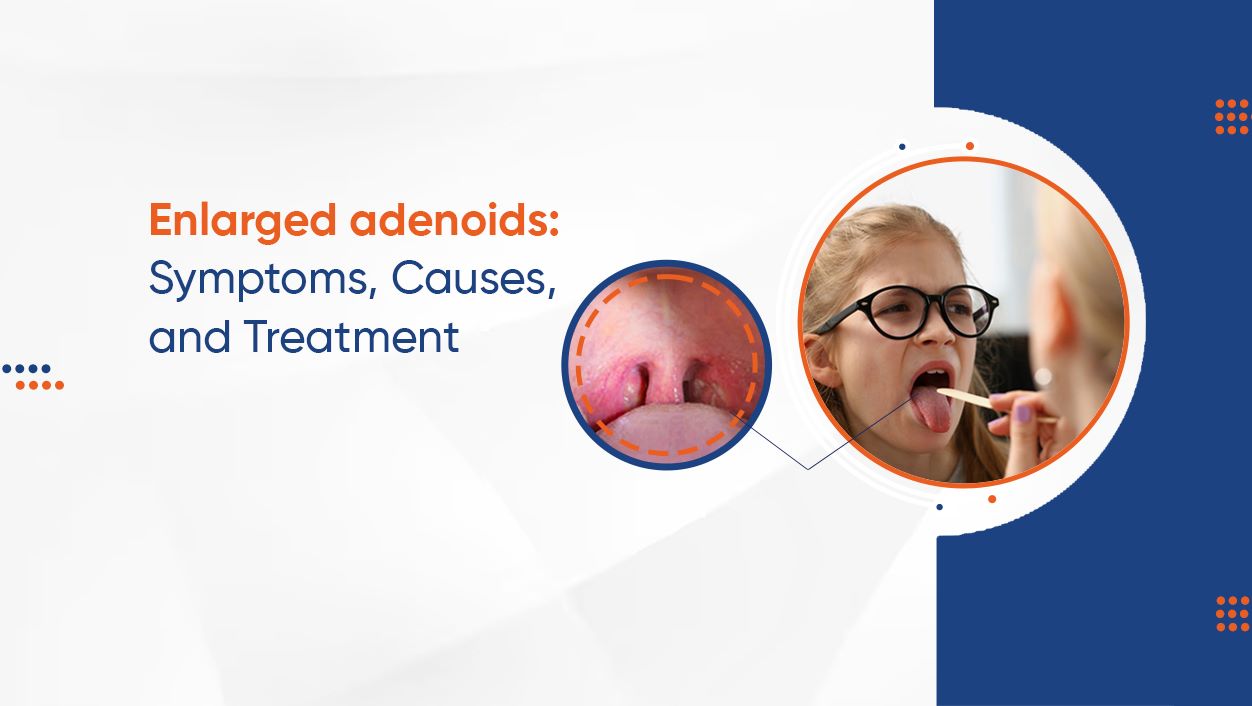
Adenoids are tiny soft tissues located above the roof of the mouth at the rear of the nasal
cavity. Adenoids, like lymph nodes, are a component of the immune system. White blood
cells pass via the adenoids to fight against infection-causing pathogens such as bacteria,
viruses, and parasites.
Adenoids are present from birth and often develop larger between the ages of 2 and 4.
Adenoids usually vanish by the time a child reaches adolescence. Adenoids can develop
larger as a result of an infection or idiopathically, producing discomfort in the youngster.
Congestion, difficulty breathing, and other signs might come from enlarged adenoids
blocking the nasal channel.
What are the signs and symptoms of adenoids that are enlarged?
Some children may not show any signs or symptoms, while others may have breathing
problems. Adenoids that are enlarged can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
1.Breathing through the nose is difficult
2.Breathing which is too loud
3.Noisy Breathing
4.Nasal congestion which persists
5.Breathing through the mouth
6.Snoring
7.During sleep, breathing comes to a halt for a few seconds
8.Breath problems
9.Mouth is parched
10.Lips that are chapped or cracked
11.Restlessness
12.Infections in the sinuses or middle ear on a regular basis.
What triggers the adenoids to enlarge?
Adenoids aid in the prevention and treatment of infections by capturing bacteria, viruses, and
other dangerous microbes, which can cause swelling. While this swelling usually goes away
on its own, these germs can sometimes trigger inflammation and infection of the adenoids, a
condition known as adenoiditis.
What are the options for treating swollen adenoids?
Most youngsters do not require treatment for swollen or diseased adenoids since they
normally shrink and vanish by the time they reach adolescence. However, in order to provide
symptom relief to the youngster, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics and decongestants.
An adenoidectomy may be recommended if you have chronic or severe breathing problems,
obstructive sleep apnea, sinusitis, or recurrent middle ear infections. Adenoidectomy is often
known as adenotonsillectomy because it involves the excision of inflammatory adenoids and
is frequently followed by the removal of tonsils. Inflammation and infection in both glands are
common after chronic throat and respiratory illnesses.
Is it possible to treat swollen adenoids at home?
Children with enlarged adenoids are more likely to acquire respiratory infections, making it
difficult for them to breathe through their noses. These symptoms, however, can be
controlled at home with several home remedies, like:
Gargles with salt water: This is one of the most common home remedies for reducing
inflammation, and pain caused by enlarged adenoids.
Turmeric : Curcumin component of turmeric, is known for its antioxidants, antibacterial,
and anti-inflammatory activities. Turmeric, when blended with warm milk, can aid in relieving
inflammation and pain.
Garlic : It includes sulfur compounds like allicin, which is antibacterial and anti-
inflammatory. By reducing inflammation, these chemicals can aid in the treatment of throat
infections. Garlic can be included in a Childs normal diet. To gain the benefits, they can be
compelled to eat a raw garlic clove first thing in the morning.
Tulsi : Holy basil, commonly known as tulsi, is said to contain antibacterial and anti-
inflammatory qualities that can help reduce adenoid swelling. A cup of hot tulsi tea can
speed up the healing process while also alleviating congestion.
Getting ready for an adenoidectomy:
Because the mouth and throat bleed more easily than other parts of the body, your doctor
may order a blood test to see if your Childs blood clots properly and if their white and red
blood counts are within normal limits. Your Childs doctor can use preoperative blood testing
to guarantee that there will be no significant bleeding during and after the treatment.
Give your child no blood-thinning medications, like ibuprofen or aspirin, in the week leading
up to surgery. Acetaminophen can be used to relieve discomfort. Consult your doctor if
you’re unsure about which drugs are right for you.
After midnight just before surgery, your child must not eat or drink anything. It includes the
use of water. If your child needs to take drugs before the procedure, give it to them with a
little sip of water.
The dangers of adenoidectomy:
Adenoidectomy is usually a painless procedure. Any operation has the risk of bleeding and
infection at the operation site. Anesthesia also carries hazards, such as adverse reactions
and respiratory difficulties.
If your kid is intolerant to any medication, make sure to tell the physician.
Conclusion:
An allergic response or a bacterial/viral infection might cause adenoids to grow. Children
with swollen adenoids frequently have respiratory problems and must breathe through their
mouths during the day. Because many persons with larger adenoids have few signs, they
don’t need therapy. However, if your Childs swollen adenoids cause sleep apnea or
repeated middle ear infections, you should see your healthcare provider.