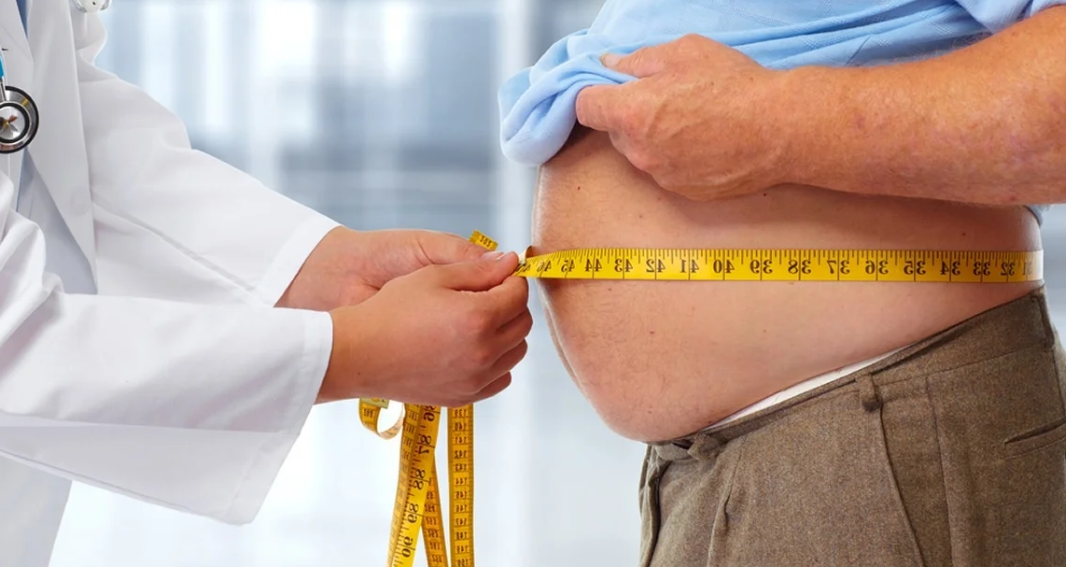
Obesity is a complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat. It is not only a cosmetic concern, it is more or less a medical problem that increases your risk to let the other diseases and health problems come in – such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure and certain cancers.
How is it caused?
In general terms – Obesity is caused by eating too much and moving too little. If you consume high amounts of energy (Fat and Sugars) but do not burn off the energy through exercise and physical activity, that surplus energy will be resting in your body as fat and never leave.
What are the risk factors of obesity?
Family inheritance and influences, No physical activity, Not having a healthy eating pattern, not maintaining sleep of 6 to 8 hrs and most importantly STRESS which could be the main reason for overweight.
Other factors
Pregnancy – Weight gain is common during pregnancy.Few of the woman find this weight very difficult to lose after the baby is born. Breast-feeding may be the best option to lose the weight gained during pregnancy.
Lack of sleep – Not getting enough sleep or getting too much sleep can cause changes in hormones that increase your appetite. You may also crave foods high in calories and carbohydrates, which can contribute to weight gain.
Saying No to smoke – To quit smoking is not that easy and at the same time is often associated with weight gain. And for some, it can lead to enough weight gain to qualify as obesity. Often, this happens as people use food to match up with their smoking habit. In the long run, to quit smoking is good for your health than continuing that habit.
Previous attempts to lose weight. Previous attempts of weight loss followed by rapid weight regain may contribute to further weight gain. This phenomenon, sometimes called yo-yo dieting, can slow your metabolism.
Other weight-related issues that may affect your quality of life include
Different mechanisms used in diets for weight loss
Reducing fat, carbohydrate (especially those with a high glycaemic index), protein or alcohol intake. Reducing alcohol intake is a very good way to lose weight, as each gram of alcohol contains a large amount of energy on top of your normal daily intake.
- Smaller portion sizes. You can try using a smaller plate size at each meal.
- Food restrictions at various times of the day. It can be helpful to have a big breakfast and reduce the intake of energy rich foods later in the day. This can help your metabolism and ensure that most of the energy that you consume is burnt throughout the day.
- Combining different foods to reduce total energy intake. Some diets have set food regimes for weight loss.
- Diets centered on a single low-energy food.
- Some exercises (especially those that require weight bearing) can be physically difficult. In this case you could try activities such as swimming, walking in water or cycling. Once your fitness levels improve you could change to other exercises in the long term.
- Behavioral therapy for weight loss –
- Self-monitoring: Identifying and recording any adverse patterns of behaviour.
- Stimulus control: This involves removing factors that encourage you to eat badly. For example, you should shop carefully and remove trouble foods (such as chocolates and chips) from the house so you cannot be tempted.
- Problem solving: Identifying and addressing problems associated with eating and physical activity. You should consider which factors have led to your excess weight and address them appropriately.
- Social support: Strong social support from your friends and family can improve weight loss. It may be beneficial for you to enrol in a commercial program which offers a social support network.
How would you prevent yourself from this?
- Exercise regularly– You need to get 150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity activity a week to prevent weight gain. Moderately intense physical activities include fast walking and swimming.
- Follow a healthy-eating plan – Focus on low-calorie, nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Avoid saturated fat and limit sweets and alcohol. Eat three regular meals a day with limited snacking. You can still enjoy small amounts of high-fat, high-calorie foods as an infrequent treat. Just be sure to choose foods that promote a healthy weight and good health most of the time.
- Know and avoid the food traps that cause you to eat – Identify situations that trigger out-of-control eating. Try keeping a journal and write down what you eat, how much you eat, when you eat, how you’re feeling and how hungry you are. After a while, you should see patterns emerge. You can plan ahead and develop strategies for handling these types of situations and stay in control of your eating behaviors.
- Monitor your weight regularly – People who weigh themselves at least once a week are more successful in keeping off excess pounds. Monitoring your weight can tell you whether your efforts are working and can help you detect small weight gains before they become big problems.
- Be consistent – Sticking to your healthy-weight plan during the week, on the weekends, and amidst vacation and holidays as much as possible increases your chances of long-term success.
Just wanted to end this article by letting you all know that we must control our body weight by changing the way we approach weight loss that can help us be more successful at weight management. Most people who are trying to lose weight focus on just the goal of weight loss. However, setting the right goals and focusing on lifestyle changes such as following a healthy eating plan, watching portion sizes, being physically active, and reducing sedentary time are much more effective.