 Cellulitis
Cellulitis
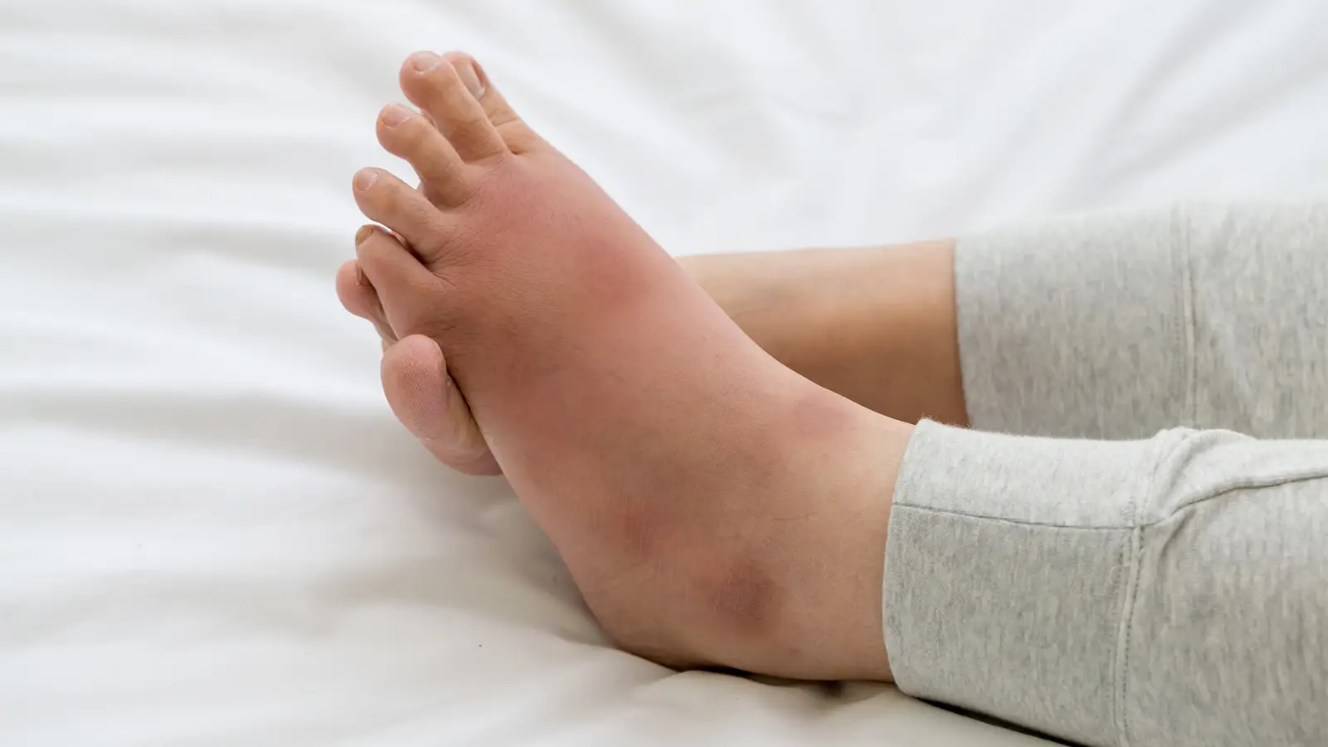
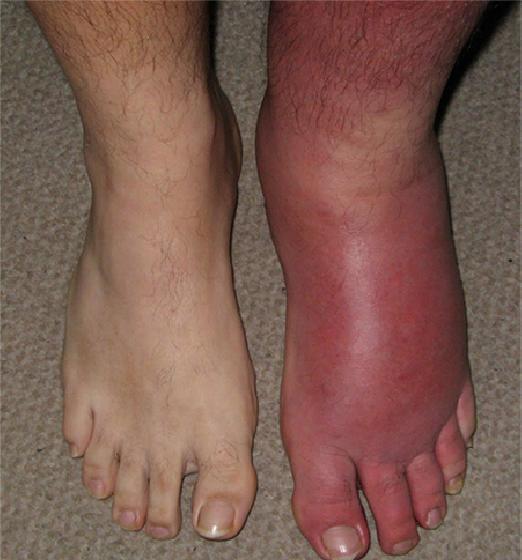
is a common and sometimes painful bacterial skin infection. It may first appear as a red, swollen area that feels hot and tender to the touch. The redness and swelling can spread quickly.
It most often affects the skin of the lower legs, although the infection can occur anywhere on a person’s body or face.
Cellulitis usually happens on the surface of the skin, but it may also affect the tissues underneath. The infection can spread to your lymph nodes and bloodstream.
If you don’t treat cellulitis, it could become life-threatening. Get medical help right away if you have symptoms.
Symptoms
- Pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Redness or inflammation of your skin
- A skin sore or rash that grows quickly
- Tight, glossy, swollen skin
- A feeling of warmth in the affected area
- An abscess with pus
- Fever
More serious cellulitis symptoms include:
- Shaking
- Chills
- Feeling ill
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Light headed-ness
- Muscle aches
- Warm skin
- Sweating
Symptoms like these could mean that cellulitis is spreading:
- Drowsiness
- Lethargy
- Blisters
- Red streaks
Causes
Cellulitis occurs when certain types of bacteria enter the skin through a cut or crack. Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bacteria can cause this infection.
The infection can start in skin injuries such as:
- cuts
- bug bites
- surgical wounds
Is cellulitis contagious?
- Cellulitis usually doesn’t spread from person to person. Yet it’s possible to catch cellulitis if you have an open cut on your skin that touches an infected person’s skin.
- If you have a skin condition like eczema (is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy. It’s common in children but can occur at any age). Bacteria can enter your skin through cracks that these conditions cause.
- A weakened immune system also increases the risk of you catching cellulitis because it can’t protect you as well against the infection.
- If you do catch cellulitis, it could be dangerous if you don’t get treated. That’s why it’s important to tell your doctor.
Home remedies for cellulitis
- Cellulitis is treated with antibiotics you get from your doctor once seen. Without treatment, it can spread and cause a life-threatening infection.
- But there are things you can do at home to relieve pain and other symptoms.
- Clean your skin in the area where you have cellulitis. Ask your doctor how to properly clean and cover your wound.
- If your leg is affected, raise it above the level of your heart. This will help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
Cellulitis risk factors
Several factors increase your risk of cellulitis, includes:
- A cut, scrape, or other injuries to the skin
- A weakened immune system
- Skin conditions that cause breaks in the skin, such as eczema and athlete’s foot
- IV drug use
- Diabetes
- History of cellulitis
- Swelling of your arms or legs (lymphedema)
- Obesity
Complications
Complications of cellulitis can be very serious if left untreated. Some complications can include:
- severe tissue damage (gangrene)
- amputation
- damage to internal organs that become infected
- shock
- death
Cellulitis and diabetes
- High blood sugar from unmanaged diabetes can weaken your immune system and leave you more vulnerable to infections like cellulitis. Poor blood flow in your legs also increases the risk.
- People with diabetes are more likely to get sores on their legs and feet. The bacteria that cause cellulitis can enter through these sores and cause infection.
- If you have diabetes, keep your feet clean. Use a moisturizer to prevent cracks. And check your feet every day for signs of infection.
Cellulitis vs. dermatitis
Dermatitis is a general term for a swollen skin rash. It’s caused by an infection or an allergic reaction, usually not by bacteria.
Contact dermatitis is an allergic reaction to an irritating substance. Atopic dermatitis is another term for eczema.
Symptoms of dermatitis include:
- red skin
- blisters that ooze or crust
- itching
- swelling
- scaling
Doctors treat dermatitis with cortisone creams and antihistamines to relieve the swelling and itching. You will also need to avoid the substance that caused the reaction.
Is there anything I can do at home for this Cellulitis infection
- Covering your wound. Properly covering the affected skin will help it heal and prevent irritation
- Keeping the area clean
- Applying a cool compress.
- Taking an over-the-counter pain reliever
- Taking all your antibiotics.