Table of Contents
Fatty Liver Disease: Everything You Need to Know
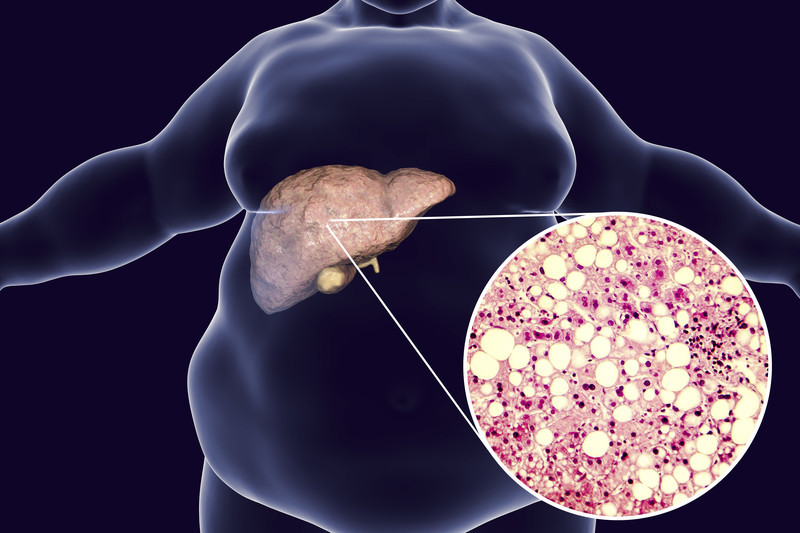
 The term “fatty liver” refers to the presence of undesired or excess fat in the liver. As per a study undertaken by the National Institutes of Health in the United States, the disorder is becoming more prevalent over the world, impacting over 25% of the world’s population. Other medical conditions linked to the syndrome include type 2 diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance disorder. Your liver cells may contain some fat in normal circumstances; but, if the amount of fat in your liver cells grows, it might cause some serious problems. It might also develop severe liver problems if left unchecked. That is why understanding the causes, signs, and management of a fatty liver is critical.
The term “fatty liver” refers to the presence of undesired or excess fat in the liver. As per a study undertaken by the National Institutes of Health in the United States, the disorder is becoming more prevalent over the world, impacting over 25% of the world’s population. Other medical conditions linked to the syndrome include type 2 diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance disorder. Your liver cells may contain some fat in normal circumstances; but, if the amount of fat in your liver cells grows, it might cause some serious problems. It might also develop severe liver problems if left unchecked. That is why understanding the causes, signs, and management of a fatty liver is critical.
The Fatty Liver: An Overview
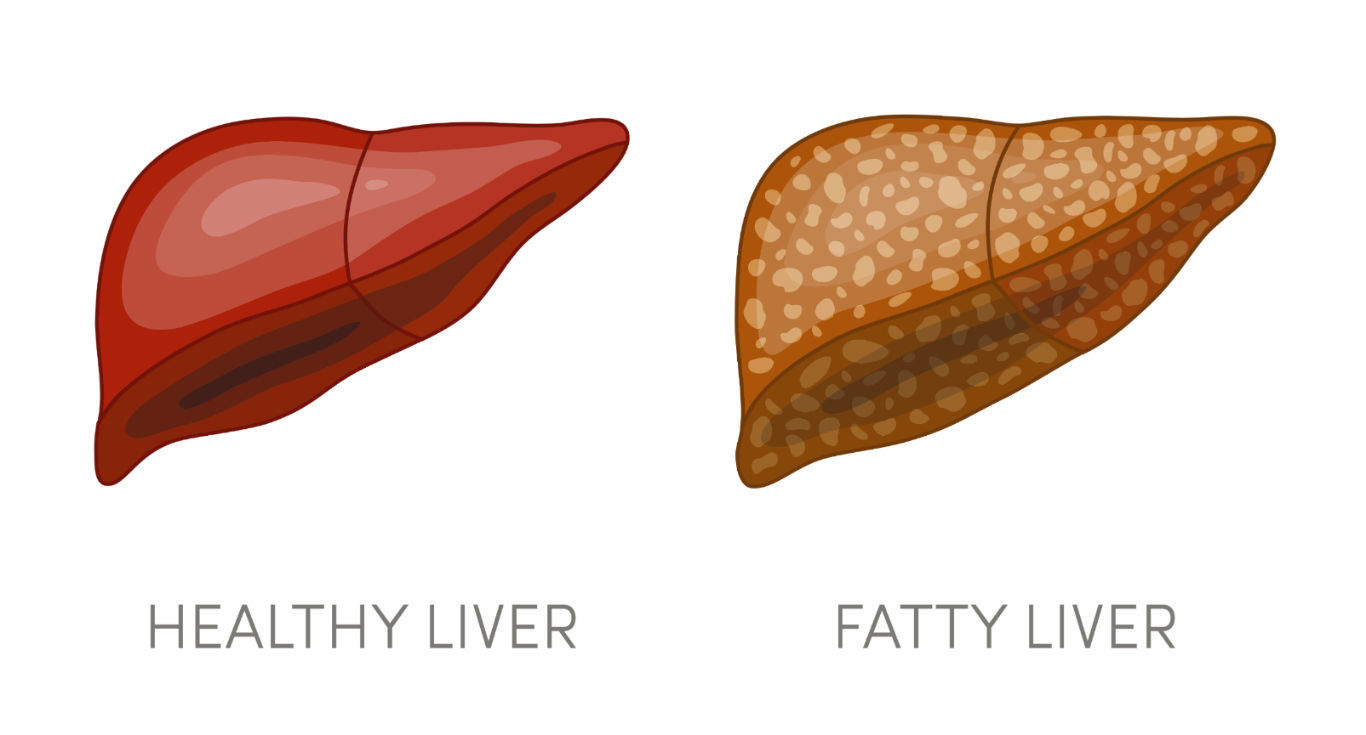
Hepatic steatosis is the clinical term for fatty liver. The liver is the second biggest organ in the body, and it is in charge of processing nutrition from food and beverages as well as filtering dangerous substances out of the body. Fatty liver is defined as having fat covering more than 5-10% of the liver. Based on the main source of the problem, fatty liver disease can be divided into two types: alcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
The fatty liver disease damages the liver severely, making it unable to eliminate poisons and generate bile as it should. If you have too much fat in your liver, it can cause scarring and inflammation, as well as liver failure.
Fatty Liver Signs:
In some circumstances, there are no obvious signs or symptoms of fatty liver. Many people may not even be aware that they have the condition. When the signs do appear, they include the following:
Weakness and exhaustion:
Mild abdominal pain, primarily to the right or center
Increased levels of liver enzymes
Insulin and lipid levels are high.
Fatty Liver: What Causes It?
It is unknown why some people acquire fat in their liver while others do not. Some variables, though, may have a part in the growth of a fatty liver, such as:
Low-grade inflammation, which is associated with obesity, promotes liver fat storage.
People who have a lot of belly fat are more likely to develop a fatty liver than those who don’t.
Insulin resistance or high insulin levels are common in people with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome, both of which increase fat storage in the liver.
Refined carbohydrate consumption significantly promotes liver fat storage, particularly in obese people.
Increased intake of sweetened drinks such as soda or energy drinks could contribute to liver fat formation due to their high fructose content.
NAFLD can also be triggered by poor gut health, leaky gut, or bacterial imbalances in the gut.
Hepatitis C, fast weight loss, contact with certain toxins, genes, and the adverse effects of some medication are some of the less prevalent causes.
Treatment for Fatty Liver:
There is now no medicine licensed as an effective therapy for fatty liver, and extensive research and medical trials are being conducted to discover and study medication that can help treat the disease. If you have a fatty liver, your doctor will most likely recommend certain lifestyle adjustments and food regimens to help you reverse the disease. The following foods and beverages can be included in a healthy liver diet:
1.Coffee consumption aids in the reduction of aberrant liver enzyme levels.
2.Greens such as sprouts, kale, broccoli, and others can help with weight loss while also preventing fat accumulation in your liver.
3.Soy protein, which can be found in foods like tofu, could also aid in fat loss.
4.Fish high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as tuna, trout, salmon, and sardines, are good for the liver.
5.Walnuts, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids, are also beneficial to the liver.
6.Avocados are high in fiber and good fats, and they also contain compounds that can help prevent liver damage.
7.Whole grains like oatmeal offer carbs that fill you up, help you maintain your weight, and give you energy, making them a perfect addition to your diet.
8.Sunflower seeds include antioxidants such as vitamin E, which protect the liver from harm.
9.Whey protein found in milk and low-fat milk products could help protect the liver from injury.
10.Garlic and olive oil are nutritious cooking ingredients that can help you lose weight and lower your liver enzyme levels.
11.Green tea aids in the reduction of fat absorption and the reduction of cholesterol levels, which aids in the improvement of liver function.
If you have a fatty liver, you would also need to avoid certain foods.
1.Alcohol is one of the most common causes of fatty liver disease and should be stopped at all costs.
2.Sugary foods, such as candies, soda, and juice, should be avoided.
3.Fried foods are high in calories and fat, thus they should be avoided where possible.
4.If you consume too much salt, your body may retain water. A daily sodium intake of 1500 mg is not recommended.
5.Red meat, as well as other foods high in saturated fats, should be avoided.
6.White bread, rice, and pasta have heavily processed flour, are low in fiber, and elevate blood glucose levels.
Fatty Liver Disease Prevention:
You can lower your chances of getting hepatic steatosis by taking the following steps:
1.Consume a nutritious plant-based diet high in good fats and whole grains.
2.Obesity might exacerbate the problem, so keep a healthy diet in mind.
3.Alcohol should be consumed in moderation or not at all.
4.Exercise for at least 30 min each day, but only after consulting with your doctor.
Fatty liver disease is not a problem to be treated lightly, as it is a significant issue that can lead to a slew of other health problems. High liver fat could be decreased by taking the correct steps, such as boosting physical activity and eating a nutritious diet, as well as minimizing the risk of future issues.